| Version 3 (modified by , 3 weeks ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
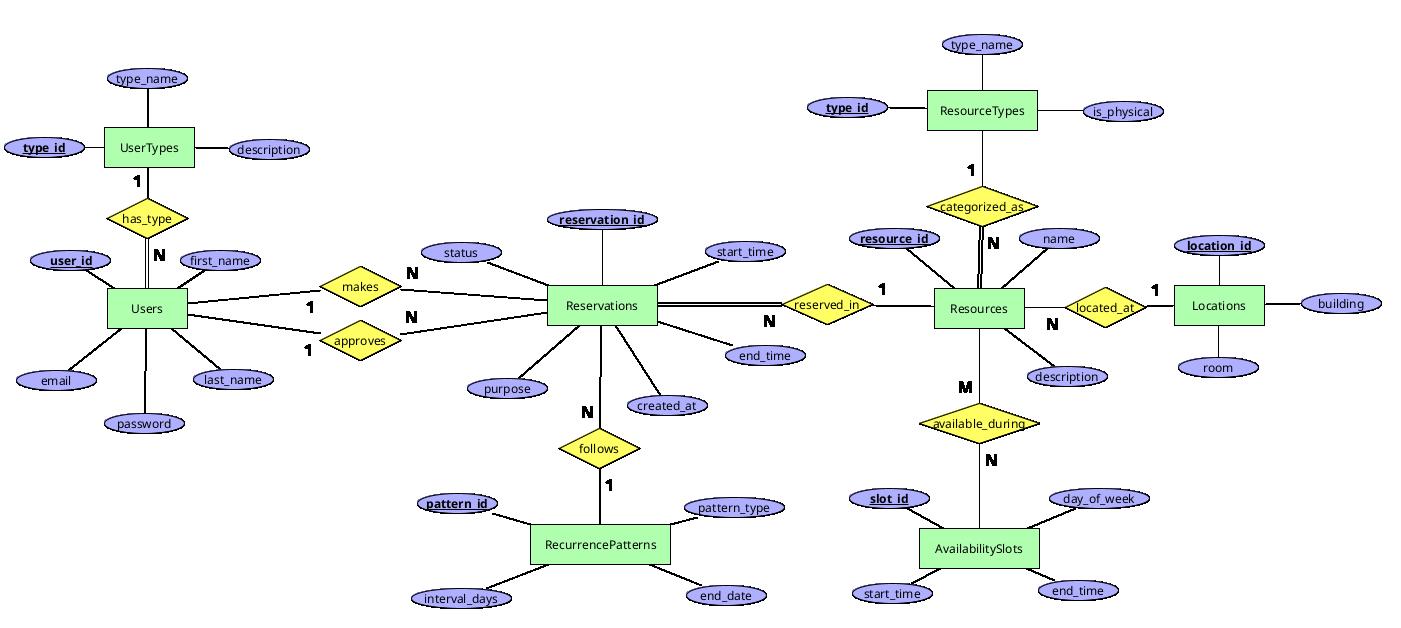
Entity-Relationship Model v.01
Diagram
Data Requirements
Entities
Users
Description: Users represents all individuals who interact with the system. This includes teaching staff who reserve resources for lectures and research, students who view availability and access permitted resources, and faculty administrators who manage the system. The entity is central to tracking who makes reservations and who approves them.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: user_id (chosen as a surrogate key for efficiency and to avoid issues with changing natural identifiers)
- Alternative candidates: email (unique per user, but may change)
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| user_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each user |
| first_name | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | User's first name |
| last_name | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | User's family name |
| VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL, UNIQUE | Institutional email address used for login | |
| password | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Hashed password for authentication |
UserTypes
Description: UserTypes categorizes users into different roles within the system. This entity enables role-based access control, distinguishing between teaching staff, students, and faculty administrators. Each role has different permissions for viewing, reserving, and managing resources.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: type_id (surrogate key for referential integrity)
- Alternative candidates: type_name (unique, but surrogate preferred for foreign key references)
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| type_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each user type |
| type_name | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL, UNIQUE | Name of the role (e.g., 'Student', 'Teaching Staff', 'Administrator') |
| description | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Detailed description of the role's permissions and purpose |
Resources
Description: Resources represents all physical and digital items that can be reserved within the faculty. Physical resources include laboratory equipment, projectors, rooms, and specialized tools. Digital resources may include software licenses, virtual machines, or online services. This entity is central to the reservation system.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: resource_id (surrogate key for efficiency)
- Alternative candidates: name (if unique within the system)
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| resource_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each resource |
| name | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Descriptive name of the resource |
| description | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Detailed description including specifications, capacity, or usage instructions |
ResourceTypes
Description: ResourceTypes categorizes resources into different types for easier navigation and filtering. Examples include 'Laboratory Equipment', 'Classroom', 'Software License', 'Projector', etc. The is_physical attribute distinguishes between physical resources (that have a location) and digital resources.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: type_id (surrogate key for referential integrity)
- Alternative candidates: type_name (unique, but surrogate preferred)
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| type_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each resource type |
| type_name | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL, UNIQUE | Name of the category (e.g., 'Projector', 'Laboratory', 'Software') |
| is_physical | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Indicates if resources of this type are physical ('Y') or digital ('N') |
Locations
Description: Locations stores information about physical places where resources can be found. This enables users to know where to pick up or use a resource. Only physical resources are linked to locations; digital resources do not require this association.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: location_id (surrogate key for efficiency)
- Alternative candidates: (building, room) composite key
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| location_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each location |
| building | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Building name or code (e.g., 'TMF', 'FINKI-A') |
| room | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Room number or name within the building |
Reservations
Description: Reservations is the core transactional entity that records each booking of a resource by a user. It tracks the time period, status (pending, approved, rejected, completed), and purpose of each reservation. This entity connects users with resources and enables conflict detection and usage analytics.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: reservation_id (surrogate key for unique identification)
- Alternative candidates: None suitable (combination of user, resource, and time could work but is complex)
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| reservation_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each reservation |
| start_time | TIMESTAMP | NOT NULL | When the reservation begins |
| end_time | TIMESTAMP | NOT NULL | When the reservation ends (must be after start_time) |
| status | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Current status: 'pending', 'approved', 'rejected', 'completed', 'cancelled' |
| purpose | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Description of why the resource is being reserved |
| created_at | TIMESTAMP | NOT NULL | When the reservation was created in the system |
AvailabilitySlots
Description: AvailabilitySlots defines recurring time windows when resources are available for reservation. Rather than storing availability for each specific date, this entity stores patterns (e.g., "Mondays 9:00-17:00") that apply weekly. This simplifies availability management and reduces data redundancy.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: slot_id (surrogate key for efficiency)
- Alternative candidates: None suitable (same day/time combination may apply to different resources)
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| slot_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each availability slot |
| day_of_week | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Day name (e.g., 'Monday', 'Tuesday') or number (1-7) |
| start_time | TIME | NOT NULL | When the availability window starts on that day |
| end_time | TIME | NOT NULL | When the availability window ends (must be after start_time) |
RecurrencePatterns
Description: RecurrencePatterns enables reservations to repeat automatically according to defined rules. This is useful for recurring events like weekly lectures or monthly equipment maintenance. Instead of creating multiple individual reservations, a single reservation can reference a pattern that defines how it repeats.
Candidate Keys:
- Primary key: pattern_id (surrogate key for unique identification)
- Alternative candidates: None suitable
Attributes:
| Attribute | Data Type | Constraints | Description |
| pattern_id | INTEGER | PK, NOT NULL | Unique identifier for each recurrence pattern |
| pattern_type | VARCHAR(128) | NOT NULL | Type of recurrence: 'daily', 'weekly', 'biweekly', 'monthly' |
| interval_days | INTEGER | NOT NULL | Number of days between occurrences |
| end_date | DATE | NULL | When the recurrence ends (NULL means indefinite) |
Relationships
has_type (Users - UserTypes)
Description: Each user is assigned exactly one user type that determines their role and permissions in the system. A user type can be assigned to many users. This is a mandatory relationship for users (total participation) since every user must have a defined role.
Cardinality: N:1 (Many users to one user type)
Participation:
- Users: Total (every user must have a type)
- UserTypes: Partial (a type may exist without assigned users)
makes (Users - Reservations)
Description: Users create reservations for resources. One user can make multiple reservations over time, but each reservation is made by exactly one user. This relationship tracks who requested each reservation.
Cardinality: 1:N (One user makes many reservations)
Participation:
- Users: Partial (not all users make reservations)
- Reservations: Total (every reservation has a creator)
approves (Users - Reservations)
Description: Faculty administrators approve or reject reservations. This relationship is separate from 'makes' to distinguish between the user who requested a reservation and the administrator who processed it. One administrator can approve many reservations.
Cardinality: 1:N (One administrator approves many reservations)
Participation:
- Users: Partial (only administrators approve)
- Reservations: Partial (pending reservations have no approver yet)
reserved_in (Reservations - Resources)
Description: Each reservation is for exactly one resource. A resource can have many reservations over time (though not overlapping for the same time period). This is a mandatory relationship for reservations since every booking must specify what is being reserved.
Cardinality: N:1 (Many reservations to one resource)
Participation:
- Reservations: Total (every reservation must be for a resource)
- Resources: Partial (a resource may have no reservations)
categorized_as (Resources - ResourceTypes)
Description: Each resource belongs to exactly one resource type for categorization purposes. This enables filtering and determines whether the resource is physical (requires location) or digital. The relationship is mandatory for resources.
Cardinality: N:1 (Many resources to one resource type)
Participation:
- Resources: Total (every resource must have a type)
- ResourceTypes: Partial (a type may exist without resources)
located_at (Resources - Locations)
Description: Physical resources are associated with a location where they can be found or used. Digital resources do not have locations. One location can house multiple resources (e.g., a lab room with multiple pieces of equipment).
Cardinality: N:1 (Many resources to one location)
Participation:
- Resources: Partial (only physical resources have locations)
- Locations: Partial (a location may have no resources assigned)
available_during (Resources - AvailabilitySlots)
Description: This many-to-many relationship defines when each resource is available for reservation. A resource can have multiple availability slots (e.g., available Monday-Friday 8:00-18:00), and the same slot pattern can apply to multiple resources.
Cardinality: M:N (Many resources to many availability slots)
Participation:
- Resources: Partial (some resources may be available anytime)
- AvailabilitySlots: Partial (slots are defined independently)
follows (Reservations - RecurrencePatterns)
Description: Reservations can optionally follow a recurrence pattern for repeating bookings. When a reservation references a pattern, the system generates or recognizes repeated occurrences according to the pattern rules. Most reservations are one-time and do not use this relationship.
Cardinality: N:1 (Many reservations to one pattern)
Participation:
- Reservations: Partial (only recurring reservations have patterns)
- RecurrencePatterns: Partial (patterns exist independently)
Entity-Relationship Model History
| Version | Date | Changes |
| v01 | 2025-01-19 | Initial version with 8 entities and 8 relationships |
Attachments (4)
- ERModel_v01.png (81.2 KB ) - added by 3 weeks ago.
- ERModel_v01.xml (33.5 KB ) - added by 3 weeks ago.
- ERModel_v02.png (68.7 KB ) - added by 33 hours ago.
- ERModel_v02.xml (27.4 KB ) - added by 33 hours ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip