| Version 9 (modified by , 2 weeks ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
Analytical and statistical querying
1. Finding routes and subroutes for arbitrary locations
This SQL query retrieves trips that include both a specified start location and end location as stops, ensuring the start location comes before the end location in the stop sequence, excluding direct routes between them unless the WHERE clause is commented out.
WITH start_location AS (
SELECT ts.trip_id, ts.stop_time
FROM trip_stops ts
WHERE ts.location_id = 100 -- ohrid
),
end_location AS (
SELECT ts.trip_id, ts.stop_time
FROM trip_stops ts
WHERE ts.location_id = 300 -- skopje
),
trips AS (
SELECT s.trip_id
FROM start_location s
JOIN end_location e ON s.trip_id = e.trip_id
WHERE s.stop_time < e.stop_time
)
SELECT
t.trip_id,
t.route_id,
r.from_location_id,
r.to_location_id,
from_loc.name AS from_name,
to_loc.name AS to_name,
to_org.company_name AS transport_company,
t.status
FROM trip t
JOIN trips tr ON t.trip_id = tr.trip_id
JOIN route r ON t.route_id = r.route_id
JOIN location from_loc ON r.from_location_id = from_loc.location_id
JOIN location to_loc ON r.to_location_id = to_loc.location_id
JOIN transport_organizer to_org ON r.transport_organizer_id = to_org.transport_organizer_id
WHERE NOT (r.from_location_id = 100 AND r.to_location_id = 300) -- commenting this line here gives ONLY SUBROUTES!
2. Transport company performance overview
This SQL query aggregates performance metrics for each transport organizer, including routes operated, trips organized, tickets sold, total revenue, average ticket price, unique customers, and average rating, sorted by total revenue in descending order.
CREATE VIEW company_performance_view AS
SELECT
to_org.company_name,
COUNT(DISTINCT r.route_id) AS routes_operated,
COUNT(DISTINCT t.trip_id) AS trips_organized,
COUNT(tk.ticket_id) AS total_tickets_sold,
SUM(COALESCE(p.total_price, 0))::double precision AS total_revenue,
AVG(COALESCE(tk.price, 0))::double precision AS avg_ticket_price,
COUNT(DISTINCT tk.account_id) AS unique_customers,
ROUND(AVG(rev.rating)::numeric, 2)::double precision AS avg_rating
FROM transport_organizer to_org
JOIN route r ON to_org.transport_organizer_id = r.transport_organizer_id
JOIN trip t ON r.route_id = t.route_id
LEFT JOIN ticket tk ON t.trip_id = tk.trip_id
LEFT JOIN review rev ON tk.ticket_id = rev.ticket_id
JOIN payment p ON tk.payment_id = p.payment_id
GROUP BY to_org.transport_organizer_id, to_org.company_name
ORDER BY total_revenue DESC;
3. Top user-purchased routes
This SQL query calculates a weighted score for routes based on ticket purchases by a specific account over the past three months (with weights of 0.5, 0.3, and 0.2 for the most recent to oldest month), returning routes with scores at or above the average, ordered by weighted score in descending order.
WITH route_weighted_usage AS (
SELECT
r.route_id,
l_from.name AS from_location,
l_to.name AS to_location,
to_.company_name AS transport_company,
SUM(
CASE
WHEN DATE_TRUNC('month', t.date_purchased) = DATE_TRUNC('month', CURRENT_DATE)
THEN 0.5
WHEN DATE_TRUNC('month', t.date_purchased) = DATE_TRUNC('month', CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '1 month')
THEN 0.3
WHEN DATE_TRUNC('month', t.date_purchased) = DATE_TRUNC('month', CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '2 months')
THEN 0.2
ELSE 0
END -- this will be used as a weighted sum to give edge to recently bought tickets
) AS weighted_score
FROM ticket t
JOIN trip tr ON t.trip_id = tr.trip_id
JOIN route r ON tr.route_id = r.route_id
JOIN location l_from ON r.from_location_id = l_from.location_id
JOIN location l_to ON r.to_location_id = l_to.location_id
JOIN transport_organizer to_ ON r.transport_organizer_id = to_.transport_organizer_id
WHERE t.account_id = 300 AND t.date_purchased >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '3 months'
GROUP BY r.route_id, l_from.name, l_to.name, to_.company_name
)
SELECT
route_id,
from_location,
to_location,
transport_company,
weighted_score
FROM route_weighted_usage
WHERE weighted_score >= (SELECT AVG(weighted_score) FROM route_weighted_usage)
ORDER BY weighted_score DESC;
4. Ticket sales revenue by weekday and route
This query analyzes completed trips to show ticket volume, total and average revenue, and route details. Useful to check trends throughout the week.
SELECT
TO_CHAR(tk.date_purchased, 'Day') AS day_of_week,
COUNT(tk.ticket_id) AS total_tickets,
SUM(p.total_price) AS total_revenue,
AVG(p.total_price) AS avg_ticket_price,
r.from_location_id,
r.to_location_id
FROM ticket tk
JOIN payment p ON tk.payment_id = p.payment_id
JOIN trip t ON tk.trip_id = t.trip_id
JOIN route r ON t.route_id = r.route_id
WHERE t.status = 'COMPLETED'
GROUP BY TO_CHAR(tk.date_purchased, 'Day'), r.from_location_id, r.to_location_id
ORDER BY total_tickets DESC;
5. Most popular destinations in the past year
This SQL query aggregates ticket data by destination over the past year, calculating total passengers, unique customers, revenue, and specific ticket types, then returns destinations with passenger counts at or above the average, ordered by total passengers in descending order.
WITH destinations AS (
SELECT
l.name AS destination,
COUNT(t.ticket_id) AS total_passengers,
COUNT(DISTINCT t.account_id) AS unique_customers,
SUM(t.price) AS total_revenue,
COUNT(st.student_ticket_id) AS student_tickets,
COUNT(ct.child_ticket_id) AS child_tickets,
l.latitude,
l.longitude
FROM location l
JOIN ticket t ON l.location_id = t.gets_off_location_id
JOIN trip tr ON t.trip_id = tr.trip_id
JOIN transport_organizer to_org ON tr.transport_organizer_id = to_org.transport_organizer_id
LEFT JOIN student_ticket st ON t.ticket_id = st.ticket_id
LEFT JOIN child_ticket ct ON t.ticket_id = ct.ticket_id
GROUP BY l.location_id, l.name, l.latitude, l.longitude
),
stats AS (
SELECT AVG(total_passengers) AS mean_passengers -- this is used to avoid hard limits
FROM destinations
)
SELECT
d.destination,
d.total_passengers,
d.unique_customers,
d.total_revenue,
d.student_tickets,
d.child_tickets
FROM destinations d, stats
WHERE d.total_passengers >= stats.mean_passengers
ORDER BY d.total_passengers DESC;
6. Top selling routes for transport organizers
This query retrieves the most popular routes for a specific transport organizer, ranking them by the number of tickets sold while also showing total revenue and average ticket price.
CREATE VIEW top_selling_routes_view AS
WITH route_stats AS (
SELECT
r.route_id,
from_loc.name AS from_location_name,
to_loc.name AS to_location_name,
to_org.company_name AS transport_organizer_name,
COUNT(tk.ticket_id) AS total_tickets_sold,
SUM(p.total_price)::numeric(38,2) AS total_revenue,
AVG(p.total_price)::numeric(38,2) AS avg_ticket_price
FROM route r
JOIN transport_organizer to_org
ON r.transport_organizer_id = to_org.transport_organizer_id
JOIN location from_loc
ON r.from_location_id = from_loc.location_id
JOIN location to_loc
ON r.to_location_id = to_loc.location_id
JOIN trip tr ON r.route_id = tr.route_id
JOIN ticket tk ON tr.trip_id = tk.trip_id
JOIN payment p ON tk.payment_id = p.payment_id
GROUP BY r.route_id, from_loc.name, to_loc.name, to_org.company_name
),
max_tickets AS (
SELECT MAX(total_tickets_sold) AS max_sold
FROM route_stats
)
SELECT rs.*
FROM route_stats rs, max_tickets mt
ORDER BY rs.total_tickets_sold DESC;
Triggers
1. Update free seats based on ticket purchase
This trigger calculates the number of available tickets after purchasing a ticket and can be tested via the application, by trying to buy new tickets.
-- TRIGGER TO UPDATE FREE SEATS
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION update_free_seats()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN
IF TG_OP = 'INSERT' THEN
UPDATE trip
SET free_seats = free_seats - 1
WHERE trip_id = NEW.trip_id;
RETURN NEW;
ELSIF TG_OP = 'DELETE' THEN
UPDATE trip
SET free_seats = free_seats + 1
WHERE trip_id = OLD.trip_id;
RETURN OLD;
END IF;
RETURN NULL;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
CREATE TRIGGER ticket_insert_update_seats
AFTER INSERT ON ticket
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION update_free_seats();
CREATE TRIGGER ticket_delete_update_seats
AFTER DELETE ON ticket
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION update_free_seats();
Here's a short example:
If we purchase 3 tickets:
We get the new seat availability:
2. Trigger to apply discount to student and child tickets
When purchasing a ticket, if its a student or a child ticket there exist special discounts. Since the application supports only buying regular tickets (covered by the application use cases), we will present how buying tickets of this type will automatically apply the discounts.
-- TRIGGER TO CALCULATE TICKET PRICE WITH DISCOUNTS CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION apply_ticket_discount() RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$ BEGIN UPDATE ticket SET price = tr.base_price - (tr.base_price * NEW.discount / 100) FROM trip tr WHERE ticket.ticket_id = NEW.ticket_id AND ticket.trip_id = tr.trip_id; RETURN NEW; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; CREATE TRIGGER apply_student_ticket_discount BEFORE INSERT ON student_ticket FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION apply_ticket_discount(); CREATE TRIGGER apply_child_ticket_discount BEFORE INSERT ON child_ticket F OR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION apply_ticket_discount();
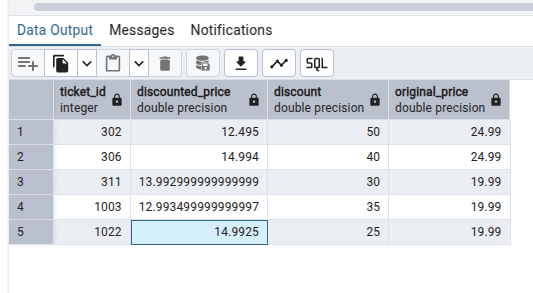
Example: If we select the existing child tickets and their appropriate base prices (i.e original prices) using a simple query:
SELECT
t.ticket_id,
t.price AS discounted_price,
ct.discount,
tr.base_price AS original_price
FROM ticket t
JOIN child_ticket ct ON ct.ticket_id = t.ticket_id
JOIN trip tr ON tr.trip_id = t.trip_id;
We will get the following results:
3. Update total payment
This trigger calculates the total payment for an account and should work together with the previous trigger for situations where we buy multiple tickets, including special types of tickets (child and student tickets). It is executed AFTER applying the discounts.
-- UPDATE TOTAL PAYMENT TOTAL PRICE (TRIGGER AFTER CHILD/STUDENT DISCOUNT IS APPLIED) CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION update_payment_total() RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$ BEGIN UPDATE payment SET total_price = ( SELECT COALESCE(SUM(price), 0) FROM ticket WHERE payment_id = NEW.payment_id) WHERE payment_id = NEW.payment_id; RETURN NEW; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; CREATE TRIGGER trg_update_payment_total_insert AFTER INSERT ON ticket FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION update_payment_total(); CREATE TRIGGER trg_update_payment_total_update AFTER UPDATE OF price, payment_id ON ticket FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION update_payment_total(); CREATE TRIGGER trg_update_payment_total_delete AFTER DELETE ON ticket FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION update_payment_total();
Attachments (4)
- trip_before.png (15.7 KB ) - added by 2 weeks ago.
- trip_after.png (7.9 KB ) - added by 2 weeks ago.
- purchase.png (3.9 KB ) - added by 2 weeks ago.
- child_ticket_prices.png (30.3 KB ) - added by 2 weeks ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip