| Version 4 (modified by , 12 days ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
ER Model
Description
This page contains the ER model description and diagrams for the system.
Entity-Relationship Model Wedding_Planner
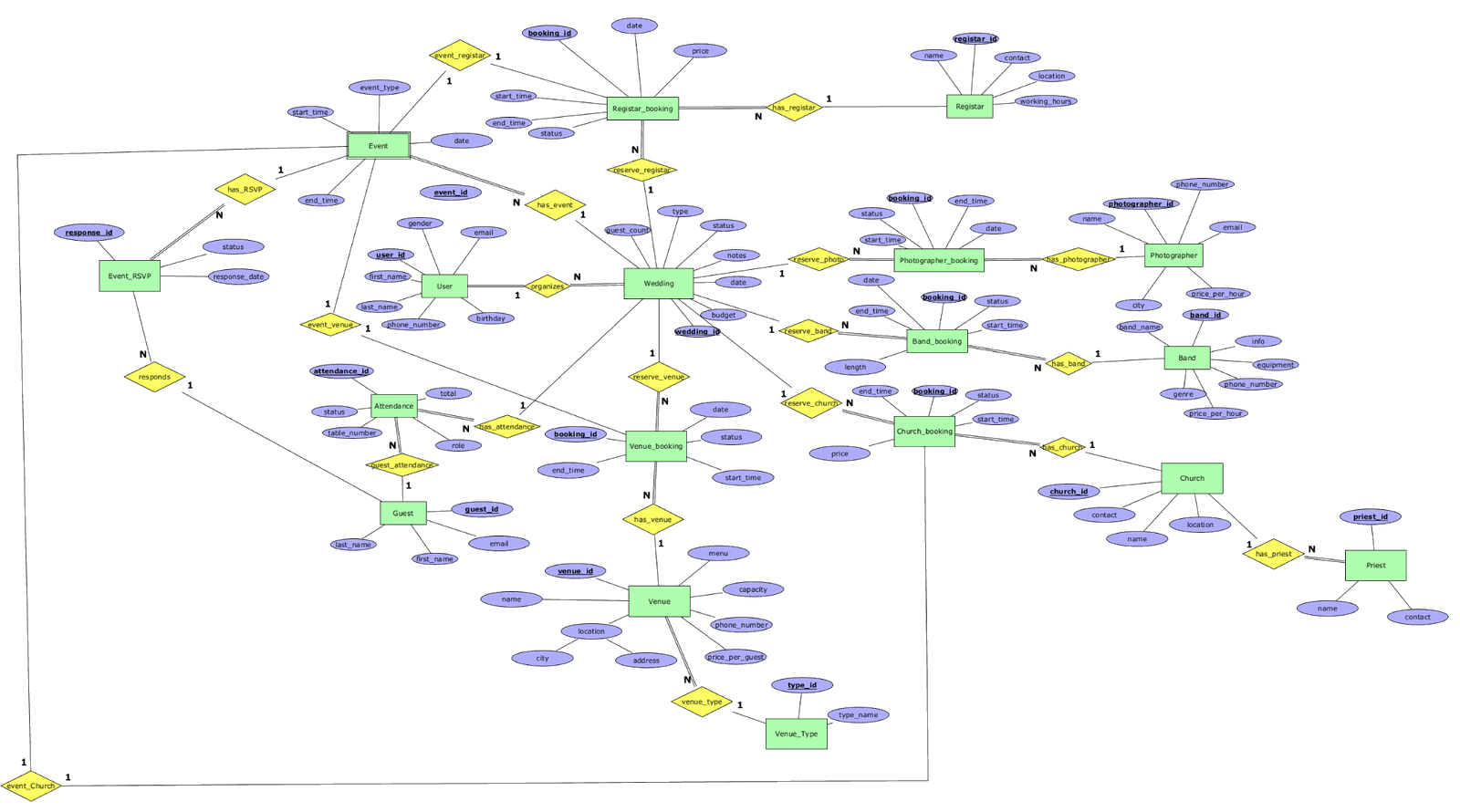
Diagram
Data requirements
Entity: User
Explanation: The User entity represents a registered person who uses the system to organize and manage weddings and related events. It stores personal and contact information and serves as the main actor that creates weddings, organizes events, and interacts with guests and service providers. The entity is modeled separately to centralize user data and enable secure identification and ownership of weddings.
Candidate keys: user_id – chosen as the primary key because it is a system-generated, stable, and unique identifier. email – candidate key because it is unique per user, but not selected as the primary key since it can change.
Attributes: user_id – numeric, required first_name – text, required last_name – text, required email – text, required, valid email format phone_number – text, optional gender – text, optional birthday – date, optional
Entity: Wedding
Explanation: The Wedding entity represents a specific wedding event being planned and managed in the system. It acts as the central entity that connects all reservations, services, guests, and events related to a wedding. It is modeled as a separate entity to clearly group all wedding-related data and enable independent management of multiple weddings by different users.
Candidate keys: wedding_id – chosen as the primary key as a unique system-generated identifier.
Attributes: wedding_id – numeric, required date – date, required budget – numeric, optional notes – text, optional
Entity: Event
Explanation: The Event entity represents individual events related to a wedding, such as ceremonies, receptions, or parties. It allows the system to track schedules, types, and statuses of events. Modeling events separately enables flexibility in planning multiple events for a single wedding.
Candidate keys: event_id – chosen as the primary key because it uniquely identifies each event.
Attributes: event_id – numeric, required event_type – text, required date – date, required start_time – time, required end_time – time, required status – text, required
Entity: Event_RSVP
Explanation: The Event_RSVP entity records responses of guests to event invitations. It is necessary to track attendance confirmations and response statuses for proper event organization.
Candidate keys: response_id – chosen as the primary key as it uniquely identifies each RSVP response.
Attributes: response_id – numeric, required status – text, required response_date – date, required
Entity: Guest
Explanation: The Guest entity represents individuals invited to the wedding. It stores guest-specific information independently from registered users, as guests do not need system accounts.
Candidate keys: guest_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: guest_id – numeric, required first_name – text, required last_name – text, required email – text, optional
Entity: Attendance
Explanation: The Attendance entity represents the participation of guests in wedding events. It is used to track whether a guest will attend a specific event, and (when applicable) their seating assignment and role during that event. Seating information is optional because not all events require tables (e.g., church ceremony or civil registration).
Candidate keys: attendance_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: attendance_id – numeric, required status – text, required table_number – numeric, optional role – text, required
Entity: Venue
Explanation: The Venue entity represents physical locations where wedding events take place. It stores capacity, pricing, and contact details to support venue selection and booking.
Candidate keys: venue_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: venue_id – numeric, required name – text, required location – text, required city – text, required address – text, required capacity – numeric, required menu – text, optional phone_number – text, optional price_per_guest – numeric, required
Entity: Venue_Type
Explanation: The Venue_Type entity categorizes venues (e.g., restaurant, hall, outdoor space). It is separated to ensure data consistency and easy extensibility.
Candidate keys: type_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: type_id – numeric, required type_name – text, required
Entity: Venue_booking
Explanation: The Venue_booking entity represents reservations of venues for weddings. It captures scheduling and pricing information and ensures no booking conflicts occur.
Candidate keys: booking_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: booking_id – numeric, required date – date, required start_time – time, required end_time – time, required status – text, required price – numeric, required
Entity: Photographer
Explanation: The Photographer entity represents professional photographers available for weddings. It stores contact and pricing information to support booking and comparison.
Candidate keys: photographer_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: photographer_id – numeric, required name – text, required email – text, required phone_number – text, required price_per_hour – numeric, required
Entity: Photographer_booking
Explanation: This entity records bookings of photographers for specific weddings and time periods.
Candidate keys: booking_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: booking_id – numeric, required date – date, required start_time – time, required end_time – time, required status – text, required
Entity: Band
Explanation: The Band entity represents music performers available for weddings. It allows storage of genre, equipment, and pricing information.
Candidate keys: band_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: band_id – numeric, required band_name – text, required genre – text, required equipment – text, optional phone_number – text, required price_per_hour – numeric, required
Entity: Band_booking
Explanation: The Band_booking entity represents reservations of bands for weddings, including timing and booking status.
Candidate keys: booking_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: booking_id – numeric, required date – date, required start_time – time, required end_time – time, required status – text, required
Entity: Church
Explanation: The Church entity represents religious locations where wedding ceremonies can take place.
Candidate keys: church_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: church_id – numeric, required name – text, required location – text, required contact – text, required
Entity: Priest
Explanation: The Priest entity represents clergy members who perform wedding ceremonies. It is modeled separately to allow assignment to church ceremonies.
Candidate keys: priest_id – chosen as the primary key.
Attributes: priest_id – numeric, required name – text, required contact – text, required
Relationships and Constraints
User – Wedding
- One User can create/manage many Weddings (1:N).
- Each Wedding belongs to exactly one User (mandatory).
Wedding – Event
- One Wedding has many Events (1:N).
- Each Event belongs to exactly one Wedding (mandatory).
Wedding – Guest
- One Wedding invites many Guests (1:N) (or M:N if a guest can be reused across multiple weddings).
- Each Guest is linked to one Wedding (if guests are not reused).
Guest – Event (RSVP)
- Guest can RSVP to many Events and each Event can have many RSVPs (M:N).
- Event_RSVP is the associative entity that stores: status, response_date.
Guest – Event (Attendance)
- Guest can attend many Events and each Event has many Attendance records (M:N).
- Attendance stores per-event guest details: role, table_number (optional), status.
Wedding – Venue_booking – Venue
- One Wedding can have many Venue_bookings (1:N).
- One Venue can be booked many times (1:N).
- Venue_booking resolves M:N between Wedding and Venue and stores date/time/status/price.
- Constraint: a Venue cannot be booked in overlapping time intervals.
Wedding – Band_booking – Band
- One Wedding can have many Band_bookings (1:N).
- One Band can be booked many times (1:N).
- Constraint: no overlapping bookings for the same Band.
Wedding – Photographer_booking – Photographer
- One Wedding can have many Photographer_bookings (1:N).
- One Photographer can be booked many times (1:N).
- Constraint: no overlapping bookings for the same Photographer.
Wedding – Church
Each Wedding is associated with exactly one Church (1:1). Each Church is associated with at most one Wedding for a given date and time. This relationship reflects the real-world assumption that a wedding ceremony is held in a single church. Since the relationship is 1:1 and no additional booking-specific attributes are required, a separate Church_booking entity is not needed. Constraint: a Church cannot be assigned to more than one Wedding at the same date and time.
Entity-Relationship Model History
*.01 – Initial version of the ER model
Attachments (3)
- Wedding_planner_Version.01.png (81.8 KB ) - added by 3 weeks ago.
- Wedding_Planner_Verison1.xml (105.1 KB ) - added by 3 weeks ago.
- Wedding_planner_Version.02.png (243.5 KB ) - added by 10 days ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip