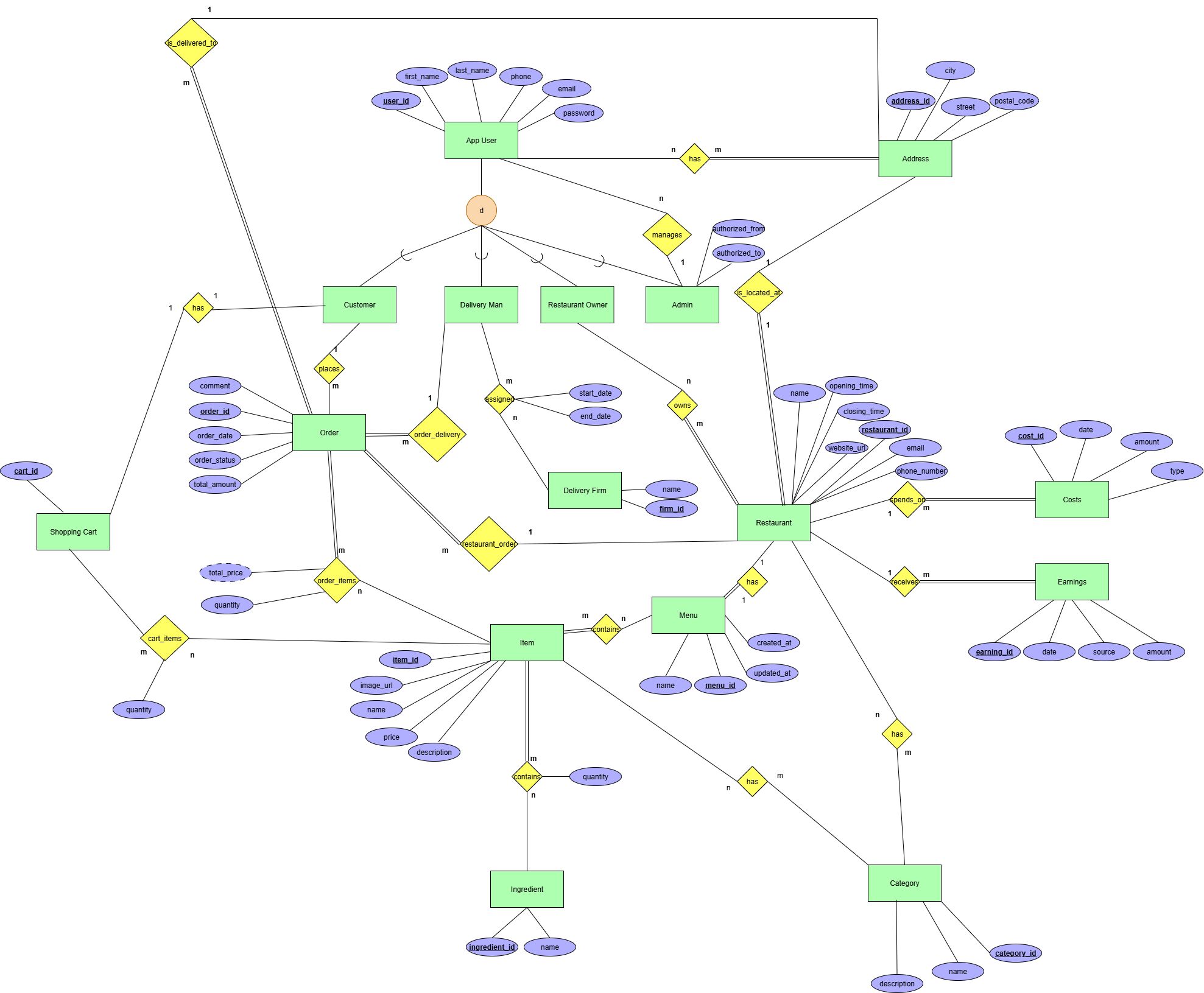
ER Diagram
Data Requirements
Entities
1. App User - Entity for all users in the system
- user_id – primary key, numeric, required
- administrator_id - foreign key, required
- first_name – text type, required
- last_name - text type, required
- phone - text type, required
- email - text type, required
- password - text type, required
2. Customer
- (No extra attributes, inherits from User)
3. Delivery Man
- (No extra attributes, inherits from User)
4. Restaurant Owner
- (No extra attributes, inherits from User)
5. Order
- order_id – primary key, numeric, required
- user_id - foreign key, required
- address_id - foreign key, required
- restaurant_id - foreign key, required
- deliveryman_id - foreign key, required
- order_date – date, required
- order_status - text type, required
- comment - text type, required
- total_amount - numeric type
6. Order Items
- order_id - foreign key, required
- item_id - foreign key, required
- quantity - numeric type, required
- total_price- numeric type, required
7. Item
- item_id - primary key, numeric, required
- name- text type, required
- description - text type, required
- price - numeric type, required
- image_url - text type, optional
8. Menu
- menu_id- primary key, numeric, required
- restaurant_id - foreign key, required
- name- text type, required
- created_at - date, required
- updated_at- date, required
9. Restaurant
- restaurant_id - primary key, numeric, required
- address_id - foreign key, required
- name - text type, required
- email - text type, required
- phone_number - text type, required
- website_url - text type, required
- opening_time - time, required
- closing_time - time, required
10. Restaurant Owners
- restaurantowner_id - foreign key, required
- restaurant_id - foreign key, required
11. Delivery Assignment
- deliveryfirm_id - foreign key, required
- deliveryman_id - foreign key, required
- start_date - date, required
- end_date - date, required
12. Delivery Firm
- firm_id - primary key, numeric, required
- name - text type, required
13. Earnings
- earning_id - primary key, numeric, required
- restaurant_id - foreign key, required
- date - date, required
- source - text type, required
- amount - numeric type, required
14. Costs
- cost_id- primary key, numeric, required
- restaurant_id - foreign key, required
- date - date, required
- type - text type, required
- amount - numeric type, required
15. Item Ingredient
- item_id - foreign key, required
- ingredient_id - foreign key, required
- quantity - numeric type, required
16. Ingredient
- ingredient_id - primary key, numeric, required
- name - text type, required
17. Address
- address_id - primary key, numeric, required
- city - text type, required
- street - text type, required
- postal_code - text type, required
18. User Addresses
- address_id - foreign key, required
- user_id - foreign key, required
19. Category
- category_id - primary key, numeric, required
- name - text type, required
- description - text type, required
20. Item Category
- item_id - foreign key, required
- category_id - foreign key, required
21. Restaurant Category
- restaurant_id - foreign key, required
- category_id - foreign key, required
22. Administrator
- user_id - primary key, numeric, required
- authorized_from - date, required
- authorized_to - date, required
23. Menu Item
- menu_id - foreign key, required
- item_id - foreign key, required
24. Shopping Cart
- cart_id - primary key, numeric, required
25. Cart Items
- cart_id - foreign key, required
- item_id - foreign key, required
- quantity - numeric type, required
Relations
1:1
- Restaurant → Menu
has – a relation which indicates that a restaurant has one menu and a menu belongs to only one restaurant.
- Address → Restaurant
is_located_at – a relation which indicates that a restaurant is located at one location, and a location can have only 1 restaurant.
- Admin → App User
manages – a relation which indicates that an admin is responsible for management of many users and a user is managed by a single admin.
- Customer → Shopping Cart
has – a relation which indicates that a customer has 1 shopping cart, and a shopping cart belongs to a user.
1:M
- Customer → Order
places – a relation which indicates that a user can have place many orders, and an order can belong to one user.
- Address → Order
is_delivered_to – a relation which indicates that an address can have multiple orders, and an order can be delivered to one address.
- Restaurant → Costs
spends_on – a relation which indicates that a restaurant can have multiple costs, and a cost belongs to one restaurant.
- Restaurant → Earnings
receives – a relation which indicates that a restaurant can have multiple earnings, and an earning belongs to one restaurant.
- Restaurant → Order
resaturant_order – a relation which indicates that a restaurant can have multiple orders, and an order belongs to one restaurant.
- Delivery Man → Order
resaturant_order – a relation which indicates that a delivery man can have multiple orders, and an order belongs to one delivery man.
M:N
- User ↔ User Addresses ↔ Address
Junction: User Addresses solves M:N relation of User and Address, by storing the composite key (user_id, address_id)
has – relation between User and Address where a user can have multiple addresses and an address can belong to multiple users.
- Order ↔ Order Items ↔ Item
Junction: Order Items solves M:N relation of Order and Item, by storing the composite key (order_id, item_id)
has – relation between Order and Item where an order can have multiple items and an item can belong to multiple orders.
- Delivery Man ↔ Delivery Assignment ↔ Delivery Firm
Junction: Delivery Assignment solves M:N relation of Delivery Man and Delivery Firm, by storing the composite key (deliveryman_id, deliveryfirm_id)
assigned – relation between Delivery Man and Delivery Firm where a delivery man can be assigned to multiple firms and a firm can have multiple delivery men.
- Restaurant Owner ↔ Restaurant Owners ↔ Restaurant
Junction: Restaurant Owners solves M:N relation of Restaurant Owner and Restaurant, by storing the composite key (user_id, restaurant_id)
owns – relation between Restaurant Owner and Restaurant where a restaurant owner can own multiple restaurants and a restaurant can have multiple owners.
- Item ↔ Item Ingredient ↔ Ingredient
Junction: Item Ingredient solves M:N relation of Item and Ingredient, by storing the composite key (item_id, ingredient_id)
contains – relation between Item and Ingredient where an item can have multiple ingredients and an ingredient can belong to multiple items.
- Item ↔ Item Category ↔ Category
Junction: Item Category solves M:N relation of Item and Category, by storing the composite key (category_id, item_id)
has – relation between Item and Category, where a category can have multiple items and an item can belong to multiple categories.
- Restaurant ↔ Restaurant Category ↔ Category
Junction: Restaurant Category solves M:N relation of Restaurant and Category, by storing the composite key (category_id, restaurant_id)
has – relation between Category and Restaurant Category, where a category can have multiple restaurants, and a restaurant can belong to mutliple categories.
- Menu ↔ Menu Item ↔ Item
Junction: Menu Item solves M:N relation of Menu and Item, by storing the composite key (menu_id, item_id)
contains – relation between Menu and Item where an item can belong to many menu's and a menu can have many items.
- Shopping Cart ↔ Shopping Cart Items ↔ Item
Junction: Shopping Cart Items solves M:N relation of Shopping Cart and Item, by storing the composite key (cart_id, item_id)
cart_items – relation between Shopping Cart and Item where an item can belong to many shopping cart's and a shopping cart can have many items.
Attachments (1)
- FINAL_DIAGRAM.jpg (212.8 KB ) - added by 7 weeks ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip