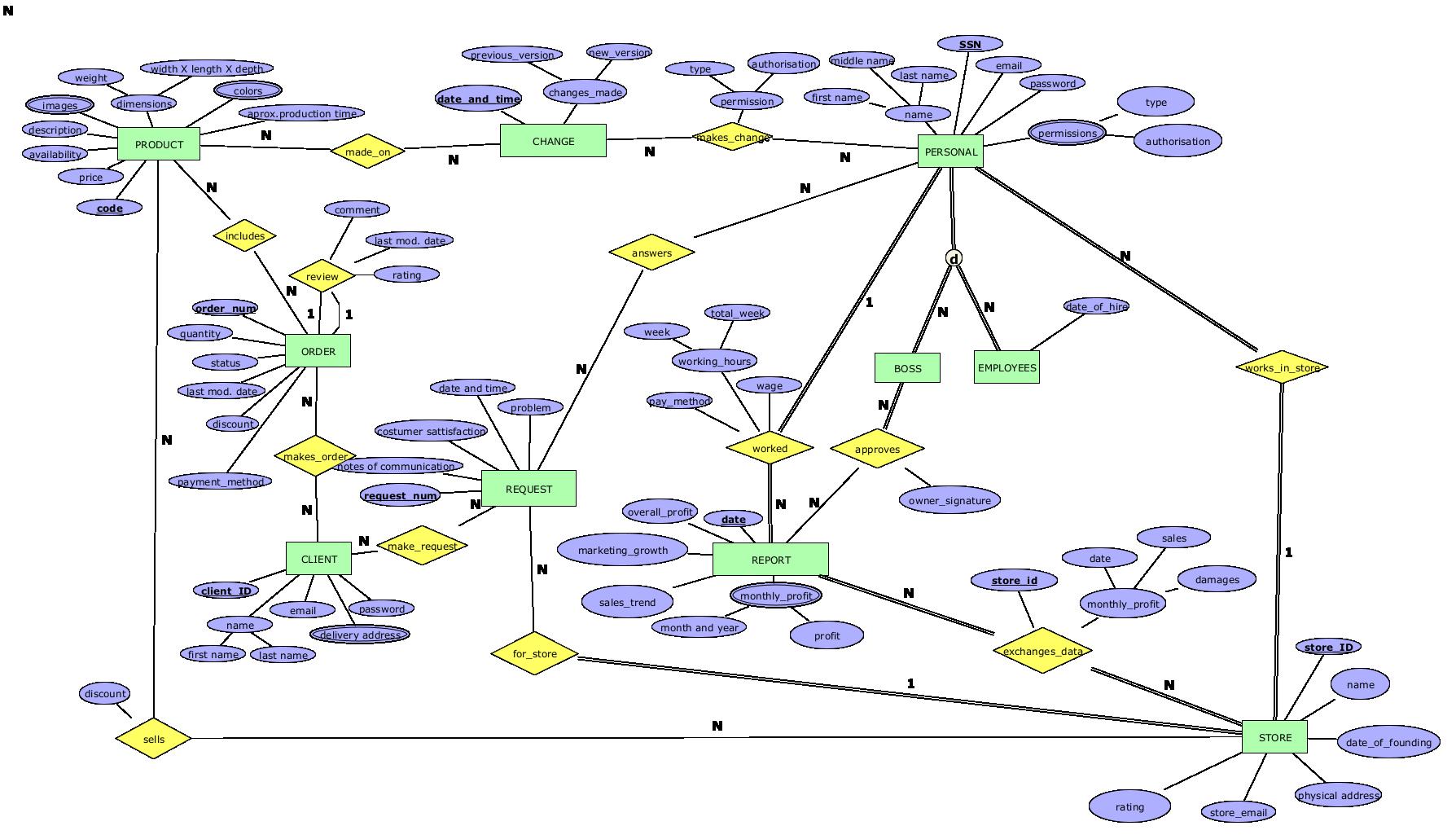
ERModel Current version
Diagram
Data requirements
ENTITIES
PRODUCT
Represents every product is currently selling by a store in the marketplace.
Candidate keys:
code– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
Attributes:
code– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.price– numeric, required.availability– numeric, required.description– text, required.images– multi-valued, media, required.dimensions– complex, text, required.weight– numeric, required.width_X_length_X_depth– text, required.colors– multi-valued, text, required.approx_production_time– numeric, required. Expressed in days.
PERSONAL
Represents each individual member of the personnel in the store.
Candidate keys:
SSN– numeric identifier (primary key).
Attributes:
SSN– numeric, required. Primary key.name– complex, text, required.first_name– text, required.last_name– text, required.middle_name– text, optional.email– text, required.password– hash value, required.permissions– complex, multi-valued, text, required.type– text, required.authorisation– text, required.
BOSS
Represents the boss/supervisor role. Inherited from PERSONAL.
Candidate keys:
SSN– inherited primary key.signature- boss' signature for authorising Reports and Permissions.
EMPLOYEES
Represents employees. Inherited from PERSONAL.
Candidate keys:
SSN– inherited primary key.
Attributes:
date_of_hire– date, required.
STORE
Represents a store registered in the marketplace system.
Candidate keys:
store_ID– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
Attributes:
store_ID– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.name– text, required.date_of_founding– date, required.physical_address– text, required.store_email– text, required.rating– numeric, optional.
CLIENT
Represents customers who are registered users for the marketplace.
Candidate keys:
client_ID– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
Attributes:
client_ID– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.name– complex, text, required.first_name– text, required.last_name– text, required.email– text, required.password– hash value, required.delivery_address– multi-valued text, required.
REQUEST
Represents customer requests or inquiries.
Candidate keys:
request_num– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
Attributes:
request_num– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.date_and_time– timestamp, required.problem– text, required.notes_of_communication– text, optional.customer_satisfaction– text, optional.
CHANGE
Represents changes made to products or systems.
Candidate keys:
date_and_time– timestamp identifier (primary key).
Attributes:
date_and_time– timestamp, required. Primary key.product_code- numeric, required.changes_made– text, required.
CASCADE
ORDER
Represents customer orders.
Candidate keys:
order_num– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
Attributes:
order_num– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.quantity– numeric, required.status– text, required.last_modified_date– timestamp, required.payment_method– text, required.discount– numeric, optional.
REPORT
Represents business reports and analytics.
Candidate keys:
date– date identifier (partial key).store_ID– surrogate numeric identifier (foreign partial key), gotten from STORE entity.
Attributes:
date– date, required. Partial primary key.store_ID– numeric, required. Foreign partial key.overall_profit– numeric, required. Profit of the store from date of founding.monthly_profit– complex, multi-valued, numeric, required.month_and_year– text, required.profit– numeric, required.sales_trend– text, optional.marketing_growth– text, optional.owner_signature– text, required.
RELATIONS
review (ORDER)
Represents reviews for orders.
Keys:
(order_num)
Attributes:
comment– text, required.rating– numeric, required.last_modified_date– timestamp, required.
works_in_store (PERSONAL – STORE)
Represents personnel working in stores.
Keys:
Composite key: (SSN, store_ID).
worked (PERSONAL – REPORT)
Tracks personnel work reports.
Keys:
Composite key: (SSN, date, store_ID).
Attributes:
week– numeric, required.total_week– numeric, required. Total hours worked that certain week.pay_method– text, required.wage– numeric, required.working_hours– numeric, required.
make_request (CLIENT – REQUEST)
Represents clients making requests.
Keys:
Composite key: (client_ID, request_num).
answers (REQUEST – PERSONAL)
Represents personnel answering requests.
Keys:
Composite key: (request_num, SSN).
makes_change (PERSONAL – CHANGE)
Represents personnel making changes to products when they have a certain permission.
Keys:
Composite key: (SSN, date_and_time).
Attributes:
permission– complex, text, required.type– text, required.authorisation– text, required.
made_on (PRODUCT – CHANGE)
Represents changes made on products.
Keys:
Composite key: (code, date_and_time).
exchanges_data (REPORT – STORE)
Represents data exchange between reports and stores.
Keys:
Composite key: (date, store_ID).
Attributes:
store_ID- numeric, required.monthly_profit– numeric, required.sales– numeric, required.damages– numeric, required.
sells (PRODUCT – STORE)
Represents products being sold in stores.
Keys:
Composite key: (code, store_ID).
Attributes:
quantity– numeric, required.discount– numeric, optional.
approves (REPORT – BOSS)
Represents bosses approving reports.
Keys:
Composite key: (date, SSN).
includes (PRODUCT – ORDER)
Represents products included in orders.
Keys:
Composite key: (code, order_num).
makes_order (CLIENT – ORDER)
Represents clients making orders.
Keys:
Composite key: (client_ID, order_num).
for_store (REQUEST – STORE)
Represents requests made for specific stores.
Keys:
Composite key: (request_num, store_ID).
ERModel History
First submitted on 09.12.2025
Edited on 17.12.2025
Last edit on 20.12.2025
Attachments (3)
-
Handcrafts-storeDB.png
(187.6 KB
) - added by 3 months ago.
ER Diagram
- Handcrafts-storeDB-Edit1.2.png (206.8 KB ) - added by 3 months ago.
- Handcrafts-storeDB-Edit1.3.png (209.2 KB ) - added by 2 months ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip