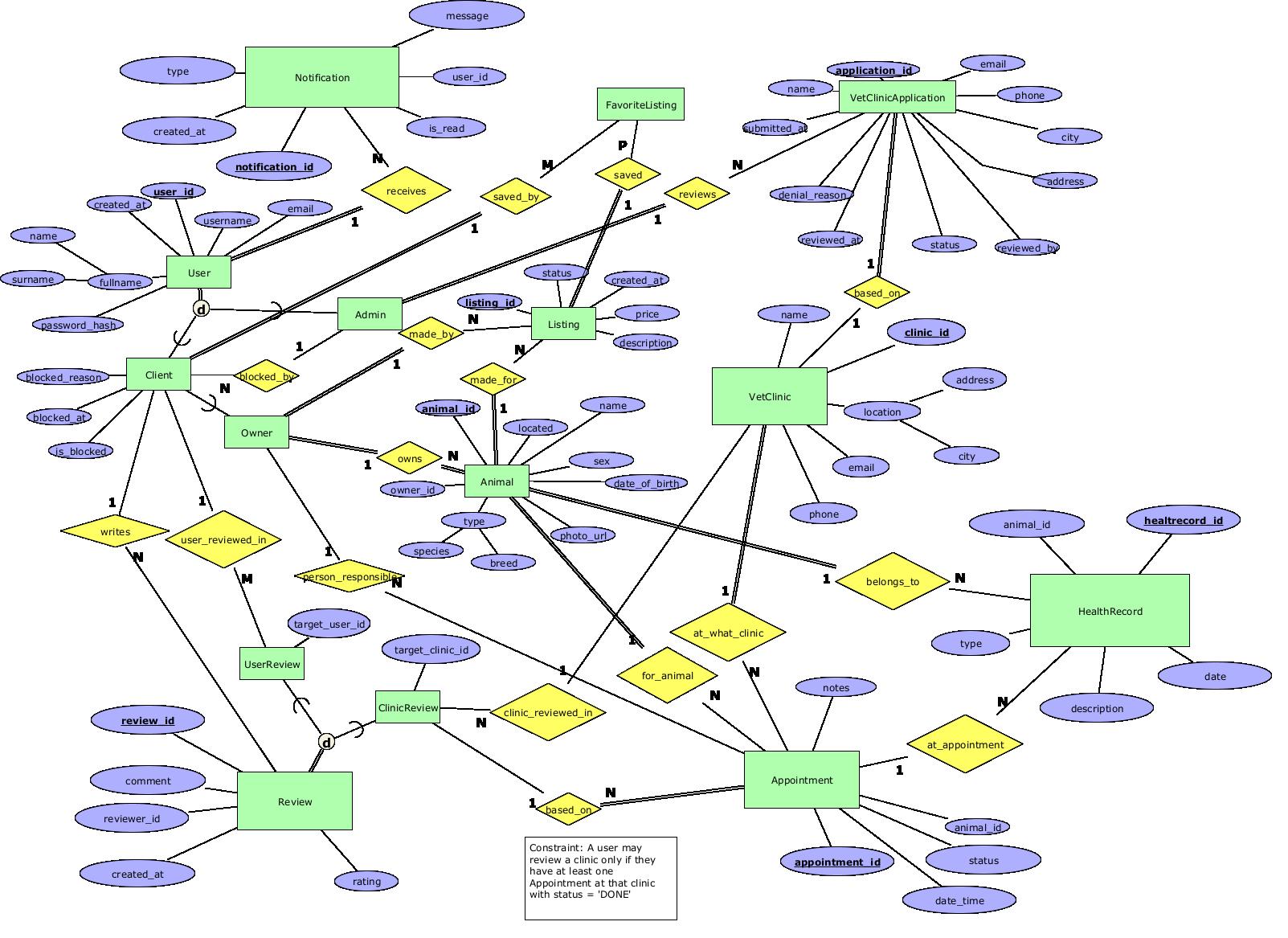
ERModel Current version
Diagram
Data requirements
ENTITIES
User
User represents every account in the system (admins and clients). It is the supertype in the user-hierarchy, holding all shared identity and login data. Modeling it as a separate entity avoids duplicating attributes in Admin/ Client/ Owner and makes authorization logic easier.
Candidate keys:
user_id– surrogate numeric identifier (chosen primary key).username– natural key, must be unique, but can change in the future.email– also unique, but might change and can be reused if a user is deleted.
user_id is chosen as PK because it is stable, short, and independent of business rules.
Attributes:
user_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated positive integer; primary key.username– text, required. Unique; max length ~30; only letters, digits and some symbols.fullname– text, required. Free-text full name.name– text, required. First name; max length ~50.surname– text, required. Last name; max length ~50.email– text, required. Must be unique; email format validation.created_at– datetime, required. Automatically set when the account is created.
Admin
Admin is a specialization of User representing accounts with administrative privileges (approving clinics, moderating listings, etc.).
Candidate keys:
user_id- inherited from User, serves as primary key and foreign key toUser
Attributes:
- No additional attributes beyond those of User.
Client
Client is the specialization for “regular” platform users (people who interact with clinics and animals). It is modeled as a subtype to distinguish them from Admins, while still sharing the common User attributes.
Candidate keys:
user_id- inherited from User, serves as primary key and foreign key toUser
Attributes:
is_blocked– boolean, required. Indicates whether the client account is currently blocked.Default value is FALSE.blocked_at– datetime, optional. Records the timestamp when the client was blocked.blocked_reason– text, optional. Stores the reason for blocking the client.blocked_by– numeric, optional. Identifies the administrator who blocked the client.
Owner
Owner is a client who actually has animals registered in the system. It’s modeled as a subtype of Client to explicitly express that only some clients own pets, and to support constraints like “only owners may book appointments”.
Candidate keys:
user_id- inherited, primary key and FK toClient(and transitively User).
Attributes:
- No additional attributes.
Listing
Represents an advertisement where a user offers an animal for sale. It is needed to separate the offer from the animal itself (the same animal can appear in multiple listings over time, and a user can create many listings). It is modeled with its own status and price attributes because these can change independently of the animal data.
Candidate keys:
listing_id– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
No realistic natural key exists that is stable and unique, so we only use listing_id.
Attributes:
listing_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.status– text, required. Allowed values like {ACTIVE, RESERVED, SOLD}.created_at– datetime, required. Date and time when the listing was created. Automatically set.price– numeric, required. Must be > 0.description– text, optional. Free-text; length limit ~ 1000 characters.
Animal
Represents each individual pet in the system. Needed to track identity, species, breed, owner, and health data independently from listings. It is modeled as a separate entity because health records, appointments, and ownership relate to the animal itself, not just to an advertisement.
Candidate keys:
animal_id– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
animal_id is chosen as PK for simplicity and stability.
Attributes:
animal_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.owner_id– numeric, required. Foreign key to User.user_id; must reference an existing user.species– text, required. Choose from predefined set.type– text, required.breed– text, required. Breed name; may be “mixed/unknown”.name– text, required. Pet name; max length ~50.sex– text, required. {MALE, FEMALE, UNKNOWN}.date_of_birth– date, required. Must not be in the future.located– text, required. City/area; free text.photo_url– text, required. URL to main photo; must be valid URL format.
VetClinic
Represents veterinary clinics that cooperate with the platform. It is needed so animals, appointments, and reviews can be associated with a specific clinic. It is modeled as a separate entity because clinics are independent organizational units with their own attributes and can be referenced by many animals, appointments, and reviews.
Candidate keys:
clinic_id– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).name + addresscould be a natural key, but both may change over time, so they are not used as the primary key.
clinic_id is chosen as PK for stability, simplicity, and immutability.
Attributes:
clinic_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.name– text, required. Clinic name; max length ~100.location– text, required. Region or district name.address– text, optional. Street address; max length ~200.city– text, required.email– text, optional. Must be valid email format; must be unique.phone– text, optional. May require a specific phone-number format.approved_by- text, which admin approved to have that clinic as a part of the app
Appointment
Represents a scheduled veterinary visit for a specific animal. Required to organize veterinary care, track upcoming visits, and link visits to clinics and generated health records. It is modeled as a standalone entity because appointments are time-based events that may create one or more medical entries.
Candidate keys:
appointment_id– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).- A composite natural key like (
animal_id,date_time,clinic_id) could be considered, but it is complex and not guaranteed unique.
appointment_id is chosen as the PK because it is simple, stable, and unambiguous.
Attributes:
appointment_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.date_time– datetime, required. Must represent a valid future or past appointment date.status– text, required. Allowed values: {SCHEDULED, COMPLETED, CANCELLED, NO_SHOW}.notes– text, optional. Additional remarks from the owner or vet.animal_id- numeric, required. Foreign key to Animal.animal_id; the animal this appointment is for.
HealthRecord
Represents a single medical action or observation (vaccination, treatment, surgery, deworming, check-up) recorded for a specific animal. It is required to maintain a complete medical history. Modeled as its own entity because multiple medical actions may occur within one appointment, and each animal can accumulate records over its lifetime.
Candidate keys:
healthrecord_id– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).- A possible natural key (
animal_id,date,type) is not reliable because multiple actions of the same type may occur on the same day.
healthrecord_id is chosen as PK for simplicity and uniqueness.
Attributes:
healthrecord_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.animal_id– numeric, required. Foreign key to Animal.animal_id.type– text, required. Allowed values include {VACCINATION, SURGERY, DEWORMING, CHECKUP}.description– text, optional. Details of the treatment or observation.date– date, required. Must be a valid date; must not be in the future for completed actions.
Review
Represents feedback written by a user about either another user (e.g., a seller) or a veterinary clinic. It is essential for trust, transparency, and reputation.
Candidate keys:
review_id– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).- A compound natural key such as (
reviewer_id,target_user_id,created_at) is possible but not guaranteed unique.
review_id is chosen as PK for simplicity and consistency.
Attributes:
review_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.comment– text, optional. Free-text comment; up to ~1000 characters.reviewer_id– numeric, required. Foreign key to User.user_id.created_at– datetime, required. Time of submission.rating– numeric, required. Integer 1–5; enforce interval [1, 5].
Special constraint:
At least one of target_user_id or target_clinic_id must be NOT NULL (exactly one in normal operation).
UserReview
UserReview is the specialization of Review used when a review is directed at a user (for example another owner, sitter, or vet user). It is modeled as a subtype of Review so that all generic review attributes (text, rating, author, time) come from the parent, while UserReview adds only the information specific to “reviews about users”, namely who the target user is.
Candidate keys:
review_id– inherited from Review and used as both primary key and foreign key toReview.review_id.
Attributes:
target_user_id– required; Foreign key to User.user_id; identifies the user being reviewed. Must reference an existing user account.
ClinicReview
ClinicReview is the specialization of Review for feedback that targets a veterinary clinic. It is a subtype of Review for the same reasons as UserReview: all generic review data is stored once in Review, while ClinicReview adds only the clinic being reviewed. This allows you to attach the special business rule “a user may review a clinic only if they have at least one DONE appointment at that clinic” specifically to ClinicReview without complicating user reviews.
Candidate keys:
review_id– inherited from Review; primary key of ClinicReview and foreign key toReview.review_id
Attributes:
target_clinic_id– required; Foreign key to User.user_id; identifies the clinic being reviewed. Must reference an existing clinic.
Notification
Represents a system-generated message delivered to a user (e.g., appointment reminders, listing updates, new reviews). It is necessary for timely communication and platform usability. It is modeled as an entity linked to a single user because each notification is specific to one recipient.
Candidate keys:
notification_id– surrogate numeric identifier (primary key).
No natural candidate key exists because notifications are numerous and non-unique.
notification_id is chosen as a primary key.
Attributes:
notification_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated primary key.type– text, required. Allowed values include {APPOINTMENT_REMINDER, NEW_REVIEW, LISTING_STATUS}.created_at– datetime, required. When the notification was generated.message– text, required. Human-readable notification body.user_id– numeric, required. Foreign key to User.user_id (recipient).is_read– boolean, required. Defaults to FALSE; becomes TRUE when viewed.
vet_clinic_applications
Represents the application a veterinary clinic submits before being approved to operate in the system.Keeping applications in a separate table supports an approval workflow without overloading the main vet_clinics entity.
Candidate keys:
application_id– surrogate numeric identifier (chosen primary key).clinic_id– unique natural identifier per clinic; one clinic can have at most one application record (as enforced by UNIQUE).application_idis chosen as PK because it is stable and independent of workflow or business changes;clinic_idremains a unique alternate key for enforcing one-application-per-clinic in this design.
Attributes:
application_id– numeric, required. Auto-generated positive integer; primary key.clinic_id– numeric, required. Unique; identifies the clinic that submitted the application.name– text, required. Clinic name as submitted; max length ~120.email– text, optional. Contact email as submitted; max length ~254; email format validation.phone– text, optional. Contact phone number as submitted; max length ~40.city– text, required. City of the clinic; max length ~80.address– text, required. Street address; max length ~200.submitted_at– datetime, required. Timestamp when the application was submitted; defaults to NOW().status– text, required. Workflow state; defaults to 'PENDING'. Allowed values: 'PENDING', 'APPROVED', 'DENIED'.reviewed_at– datetime, optional. When the application was reviewed (approved/denied).reviewed_by– numeric, optional. Admin who reviewed the application; can be NULL if reviewer is removed.denial_reason– text, optional. Explanation recorded only when status is 'DENIED'.
favorite_listings
Represents a many-to-many relationship between clients and listings, capturing which listings a client has marked as “favorite”.
Candidate keys:
(client_id, listing_id)– composite natural key (chosen primary key).
The composite key is chosen as PK because a favorite is uniquely defined by “which client favorited which listing” and no additional surrogate identifier is needed.
Attributes:
client_id– numeric, required. Identifies the client who favorites the listing.listing_id– numeric, required. Identifies the favorited listing.
RELATIONS
receives (User – Notification)
Represents that a specific user receives specific notifications. It is needed so each notification is clearly assigned to one user. The relationship is modeled as 1–N: one user can receive many notifications; each notification belongs to exactly one user.
Keys:
- Identified by
notification_id(PK of Notification). - On the relationship level, the pair (
user_id,notification_id) is unique.
Attributes:
No extra attributes apart from the foreign keys already listed: user_id in Notification.
made_by (Owner – Listing)
Links each listing to the user who created it. It is needed to track authorship, rights to modify the listing, and contact information. Modeled as 1–N because one user can create many listings, but each listing is created by exactly one user.
Keys:
- Identified by
listing_id. - The pair (
user_id,listing_id) is unique.
Attributes:
Relationship implemented via foreign key user_id inside Listing.
made_for (Listing – Animal)
Shows that a listing is created for a specific animal. It is needed to attach each advertisement to the animal being sold or adopted. Modeled as 1–N from Animal to Listing: one animal may appear in multiple listings, but each listing refers to exactly one animal.
Keys:
- Identified by
listing_id. - The combination (
listing_id,animal_id) is unique.
Attributes:
Relationship implemented through the foreign key animal_id in Listing.
owns (Owner – Animal)
Represents ownership of animals. It ensures that only the rightful owner can manage listings or initiate health-related actions. Modeled as 1–N: one user can own many animals, while each animal has exactly one current owner.
Keys:
- Identified by
animal_id. - Unique pair (
owner_id,animal_id).
Attributes:
Foreign key owner_id is stored in Animal.
approves (Admin – Listing)
Represents that a admin approves a vetclinic to be a part of the system.
person_responsible (Owner - Appointment)
Represents that an Appoinment needs to have by whom it was created by(who is the owner of the animal in that appointment).
writes (User – Review)
Represents that a user writes a review. Critical for establishing authorship and preventing anonymous reviews. Modeled as 1–N: one user can write many reviews, while each review has exactly one author.
Keys:
- Identified by
review_id. - Unique pair (
reviewer_id,review_id).
Attributes:
Foreign key reviewer_id appears in Review.
user_reviewed_in (User – UserReview)
Represents that a user is the target of a review (e.g., a seller rated by a buyer). Needed for calculating user reputation. Modeled as 1–N: one user can receive many reviews, while each review may refer to one target user.
Keys:
- Identified by
review_id. - The pair (
target_user_id,review_id) is unique.
Attributes:
Foreign key target_user_id in Review (may be NULL when reviewing a clinic).
clinic_reviewed_in (VetClinic – ClinicReview)
Represents that a clinic is the target of a review. This supports public ratings of veterinary clinics. Modeled as 1–N: one clinic can receive many reviews; each review may refer to a single clinic.
Keys:
- Identified by
review_id. - Unique pair (
target_clinic_id,review_id).
Attributes:
Foreign key target_clinic_id stored in Review (NULL if review is about a user).
belongs_to (Animal – HealthRecord)
Connects each medical record entry to the animal it describes. It is essential for maintaining a full medical history. Modeled as 1–N: one animal has many health records, while each health record refers to one animal.
Keys:
- Identified by
healthrecord_id. - Unique pair (
animal_id,healthrecord_id).
Attributes:
Foreign key animal_id is stored in HealthRecord.
at_appointment (Appointment – HealthRecord)
Represents that a health record entry was created during a specific appointment. Needed to link treatments and checkups to their corresponding visits. Modeled as 1–N: one appointment may generate many records; each record belongs to at most one appointment.
Keys:
- Identified by
healthrecord_id. - Unique pair (
appointment_id,healthrecord_id).
Attributes:
Foreign key appointment_id included in HealthRecord (may be NULL if manually added).
at_what_clinic (VetClinic – Appointment)
Represents at which veterinary clinic a given appointment takes place. This allows the system to know the location of each visit, show a clinic’s schedule, and coordinate resources. Modeled as 1–N: one clinic can host many appointments, while each appointment is held at exactly one clinic.
Keys:
- Identified by
appointment_id. - Unique pair (
clinic_id,appointment_id).
Attributes:
Foreign key clinic_id stored in Appointment.
for_animal (Animal – Appointment)
Represents which animal a given appointment is scheduled for. It is needed so every appointment is clearly tied to a specific pet, enabling the system to show that pet’s upcoming visits and history. The relationship is modeled as 1–N from Animal to Appointment: one animal can have many appointments over time, while each appointment refers to exactly one animal.
Keys:
- Identified by
appointment_id(PK of Appointment). - On the relationship level, the pair (
animal_id,appointment_id) is unique.
Attributes:
No extra attributes apart from the foreign key animal_id stored in Appointment.
based_on (ClinicReview – Appointment)
Represents that a user can't leave a review for a clinic if he hasn't had a appointment there.
ERModel History
VersionOne - Added specialization of the User entity(User became a supertype and two subtypes were added),added specialization of the Review entity, added a relationship between Owner and Appointment, added a business rule (constraint) for clinic reviews
VersionTwo - The schema was updated by adding password support for clients, introducing a vet clinic application table to handle clinic onboarding.Blocking attributes were added for clients that store the responsible admin and reason. Additionally, a favorites table was introduced to represent the relationship between clients and listings
Attachments (4)
- ERModel_v01.png (164.1 KB ) - added by 3 months ago.
- ERModel_v01.2.png (164.1 KB ) - added by 3 months ago.
- ERModel_v02.jpg (204.3 KB ) - added by 3 months ago.
- ERModel_v03.jpg (245.4 KB ) - added by 9 days ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip